Leg Drive in the Bench Press: A Complete Guide

What's In This Article
- Key Highlights
- Introduction
- Why Leg Drive Matters
- Setting Up Your Leg Drive
- Activating Leg Drive
- Training for Better Leg Drive
- How Leg Drive Enhances Shoulder Stability
- Equipment Considerations
- Advanced Techniques
- Common Problems & Solutions
- Next Steps
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key Highlights
- It is a crucial technique in bench that can significantly enhance performance
- It helps maintain upper back position, increase stability, and improve strength
- Proper foot positioning is essential for effective leg drive
- Synergizes with upper body mechanics to improve shoulder stability and increase pressing force
- Training tips and drills can help optimize leg drive and maximize its benefits in the bench press
- It is not cheating and can prevent injuries and improve performance when done correctly
Introduction
Learn how to increase your bench press by mastering leg drive - the technique powerlifters use to generate maximum force and stability through proper leg positioning and activation.
Why Leg Drive Matters
Leg drive added 40 pounds to my competition bench in 6 months
The bench press isn't just an upper body exercise. Elite powerlifters like Julius Maddox and Jennifer Thompson consistently emphasize that proper leg drive can:
- Increase stability during heavy lifts
- Enhance force transfer from ground to bar
- Improve shoulder positioning
- Reduce injury risk through better technique
Defining Leg Drive and Its Role in Lifting
- As mentioned earlier, it refers to driving the feet into the floor during the bench press. This technique is crucial in maximizing strength and stability throughout the lift. Lifters can maintain a more effective upper back position, reduce the range of motion required by the barbell, and generate greater force output.
- Various muscle groups are involved when performing the bench press, including the pectoralis major (chest muscles), deltoids (shoulder muscles), and triceps. Leg drive helps engage additional muscle groups, such as the glutes and lower back, which contribute to overall stability and force generation. By utilizing it effectively, lifters can optimize their bench press performance and lift heavier weights with greater ease. In the next section, we will explore the biomechanics behind this technique and its impact on the body during the bench press.
- Lower body involvement increases overall stability. 2023 research by Marquina et al. concluded both upper and lower body stability are crucial for optimal bench press performance, highlighting the importance of a stable base and control throughout the movement.
Biomechanics
- The biomechanics involve the interaction of several key body parts, including the lower back and knee joint. Properly executed, it creates a more mechanically advantageous position for the lifter, allowing optimal force transfer and stability.
- By driving the feet into the floor, the lifter engages the lower back, which helps maintain an arched position and increases core stability. This arched position minimizes the distance the barbell needs to travel, reducing the range of motion and allowing for greater force production.
- Additionally, leg drive activates the knee joint, leading to a more solid foundation and increased stability. This stability improves the lifter's ability to push the barbell off the chest and enhances overall strength and performance. By understanding the biomechanics, lifters can optimize their foot positioning and leverage this technique to maximize their bench press potential.
Key Takeaway: Understanding and implementing proper foot biomechanics can significantly improve bench press technique and overall lifting performance.
Setting Up Your Leg Drive
1. Foot Position Fundamentals
✅ *Correct Setup*:
- Feet flat on floor
- Shins vertical or slightly angled
- Feet about shoulder-width apart
- Heels firmly planted
❌ *Common Mistakes*:
- Feet too far back under bench
- Heels rising during press
- Unstable foot position
- Inconsistent placement
The Impact of Foot Angle on Power Generation
Proper foot positioning is essential for effective leg engagement in the bench press. Your foot position on the floor can significantly impact your ability to generate power and maintain stability during the lift. Finding the correct foot placement involves striking a balance between comfort and functionality.
A common starting point for foot placement is to have your shins vertical and your feet shoulder-width apart. From there, you can experiment with slight variations, such as moving your feet slightly closer to your shoulders or slightly more in front of you. The optimal foot placement will vary depending on your body proportions and comfort level. Finding a foot position that allows you to push through the floor effectively without compromising other aspects of your setup is important and may lead you to the most efficient position. In the following sections, we will discuss the ideal foot placement for maximum stability and the impact of foot angle on power generation.
Foot Angle Variations:
- Angle Options
- Slightly wider foot angle
- Neutral foot angle
- Personalized positioning
- Factors to Determine Optimal Foot Angle
- Personal comfort level
- Force generation capability
- Individual body mechanics
Benefits of Different Approaches:
- Wider foot angle:
- Increased strength potential
- Enhanced stability
- Better force generation (especially for powerlifters)
Recommended Strategy:
- Experiment with different foot angles
- Listen to your body
- Focus on:
- Maintaining leg drive
- Preserving balance
- Maximizing power output
Key Takeaway: There's no one-size-fits-all foot angle. The best position is the one that feels most comfortable and generates the most power for you personally.

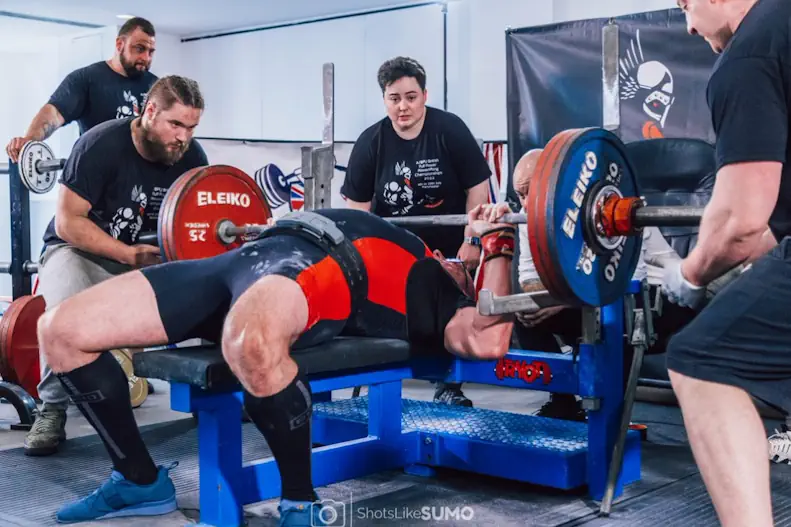
2. Creating the Power Position
Lie on bench with feet flat
- Pull shoulder blades together and down
- Create slight arch in lower back
- Push chest up toward ceiling
- Push feet into floor
💡 *Pro Tip*: Mark your foot position on the floor with chalk for consistency between sets.
Mike Tuchscherer, renowned powerlifter and coach, states:
"Proper leg drive isn't just pushing with your legs. It's about creating and maintaining tension throughout your entire body."
And Chad Wesley Smith, elite powerlifter and strength coach, emphasizes:
"Leg drive in the bench press is about maintaining position and creating full-body tension, not about driving your butt off the bench."
Activating Leg Drive
Proper leg drive involves engaging the lower body muscles to generate force against the floor. This force should be directed downward and away from your body, helping to maintain stability and create a more efficient pressing motion. To activate effectively, it is recommended to initiate leg drive before lifting the barbell out of the rack and maintaining the drive throughout each bench set.
The 3-Step Technique
1. *Initial Setup*
- Get tight before unracking
- Push feet into floor
- Feel tension in legs
2. *During Descent*
- Maintain foot pressure
- Keep upper back tight
- Control bar path
3. *Press Phase*
- Push feet forward and down
- Push body into bench
- Press explosively
⚠️ *Warning*: Never let your hips leave the bench - this is illegal in competition and reduces stability.

Training for Better Leg Drive
Here are some drills that can help enhance leg activation:
Key Exercises
- Box Squats
- Hip Thrusts
- Leg Press
- Paused Bench Press
Sample Workout
Box Squats
3 sets x 5 reps @ 70-80%
Paused Bench Press
4 sets x 3 reps @ 75-85%
Focus: Perfect leg drive each rep
Hip Thrusts
3 sets x 8 reps
Focus: Explosive power
How Leg Drive Enhances Shoulder Stability
Leg drive enhances lower body engagement and synergizes with upper body mechanics to improve overall performance. This relationship is crucial for maximizing force generation and stability.
Lifters can improve shoulder stability by maintaining maximal retraction of the shoulder blades and pushing the chest upward. This combination of drive and upper body engagement creates a more rigid and stable torso, allowing greater force transfer throughout the lift.
2024 research by Noteboom et al. investigated how different bench press techniques affect shoulder loads and potential injury risks. The researchers examined the effects of grip width, scapular position, and force application on shoulder biomechanics.
Key findings:
- Scapular retraction and appropriate grip width decreased glenohumeral posterior shear force and rotator cuff activity.
- Proper upper body positioning (scapular control) reduced the risk of glenohumeral instability and rotator cuff injuries.
- Mediolateral force components applied to the barbell significantly affected shoulder reaction forces, emphasizing the need for overall stability.
The study concluded that both upper body stability (scapular control) and overall body control (force application) are critical for reducing injury risk and optimizing bench press technique.
Core Stability Principles:
- Lower body engagement is crucial for:
- Enhancing shoulder stability
- Maintaining upper back position
Key Techniques for Shoulder Stability:
- Lower Body Positioning
- Drive feet into the floor
- Create a stable foundation
- Support upper body mechanics
- Shoulder Blade Positioning
- Maximize shoulder blade retraction
- Push chest upward
- Create optimal pressing position
- Torso Stabilization
- Provide rigidity and support
- Facilitate proper shoulder positioning
- Enhance overall lifting stability
Performance Benefits:
- Improved shoulder control
- Enhanced force transfer
- Better lifting mechanics
- Increased overall stability during bench press
Key Takeaway: Proper lower body engagement and shoulder positioning are critical for maximizing shoulder stability and performance in the bench press.

Equipment Considerations
Footwear
Best options:
- Wrestling shoes
- Powerlifting shoes
- Flat sneakers
Avoid:
- Running shoes
- Thick-soled shoes
- Unstable footwear
Bench Setup
- Proper height
- Non-slip surface
- Competition width
- Stable base
Advanced Techniques
Adjusting for Different Body Types
Body type significantly affects how leg drive is optimized in the bench press. Smaller lifters, for example, may need to adjust their technique to accommodate their size and leverage.
Adjusting foot positioning and experimenting with variations can optimize force generation and stability for smaller lifters. To maximize leg drive, some smaller lifters may benefit from a narrower stance or a more pronounced arch in the lower back.
Additionally, incorporating exercises like the leg press can help smaller lifters develop strength, allowing them to generate more power through leg drive. Smaller lifters can enhance their performance by focusing on proper form and gradually increasing the weight.
Exploring Variations in Positioning
Exploring variations in positioning can be beneficial for optimizing overall bench press performance. Adjusting the position of the legs can impact force generation, stability, and the mechanics of the lift.
Below is a table highlighting some common variations in positioning and their potential benefits:
|
Variation |
Description |
|
Wider Stance |
Placing the feet wider apart can provide a more stable base |
|
Narrower Stance |
Bringing the feet closer together may increase leg drive activation and target specific muscle groups |
|
Feet Forward |
Positioning the feet slightly in front of the shoulders can alter the torso angle and force transfer |
|
Feet Back |
Placing the feet slightly behind the shoulders may provide a more mechanically advantageous position |
Experimenting with these variations while maintaining proper form and alignment is important to find the best positioning for your body and mechanics.
Common Problems & Solutions
|
Problem |
Solution |
|
Hips rising |
Widen stance |
|
Lost tension |
Start setup over |
|
Inconsistent drive |
Practice paused reps |
|
Poor timing |
Video analysis |
Debunking the Myth of Leg Drive as Cheating
One of the most common misconceptions surrounding leg drive in the bench press is that it is considered cheating, especially in powerlifting competitions. However, this is far from the truth.
The technique is legitimate and widely accepted by powerlifters to enhance their performance. It is not against the rules and is recognized as a skilful way to generate more force and stability during the lift. In fact, neglecting it can disadvantage lifters and limit their potential for success.
Clarifying the Role in Injury Prevention
By engaging the legs and driving through the floor, lifters can establish a more efficient and stable position, minimizing unnecessary movements and reducing the risk of strain or injury. This proper engagement enhances hip mobility, and helps maintain proper form, stability, and control throughout the lift, reducing the likelihood of compensatory movements or excessive stress on certain muscle groups.
Proper foot positioning and muscle activation contribute to overall stability and strength, leading to safer bench press technique.
Dr. Mike Israetel, sports scientist and co-founder of Renaissance Periodization, explains:
"Leg drive in the bench press serves multiple purposes. It enhances stability, improves force production, and helps maintain proper shoulder positioning. All of these factors contribute to safer and more effective bench pressing."
And strength coach Jim Wendler, creator of the 5/3/1 program, advises:
"Don't neglect your lower body in the bench press. Proper foot placement and leg drive are key to creating full-body tension and stability. This allows you to press more weight with better form and reduced injury risk."
Next Steps
- Video your current bench setup
- Practice setup without weight
- Gradually incorporate with light weights
- Film progress weekly
- Join our community for form checks
Frequently Asked Questions
How much can leg drive add to my bench?
Most lifters see 5-15% improvement with proper technique.
Is leg drive cheating?
No - it's a legal and essential technique in powerlifting.
How long to master leg drive?
A: 4-8 weeks of consistent practice for basic proficiency.
Are there any specific techniques for optimizing leg drive during the bench press?
Proper foot placement, initiating leg drive before lifting the barbell, maintaining engagement throughout the lift, and focusing on pushing "down and away" from the body can all help optimize the drive. Experimenting with foot angle and foot positioning can also help.
Can improper use of leg drive lead to injuries during the bench press?
Improper use can potentially lead to injuries. Lifting the glutes off the bench or using excessive leg drive without proper form and stability can compromise technique and increase the risk of strain or injury in any federation. Maintaining proper form and technique while employing leg drive is important to minimize the risk of injuries.